Virtual Reality is one of the technologies revolutionizing research in the Physical Rehabilitation field. VR is one of the exciting approaches increasingly in use in improving patient outcomes. Once mainly used in the entertainment industry, VR has evolved over the years. It is becoming a core part of the strategies used in the rehabilitation of injuries, surgery, and long-term conditions. This paper undertakes a comprehensive review on how VR is incorporated into a rehabilitation setting, patients’ gains, and the technology implemented. The analysis is further supported by the views of healthcare practitioners and patients as primary sources of data on the topic.
Rehabilitative Physical Therapy using VR
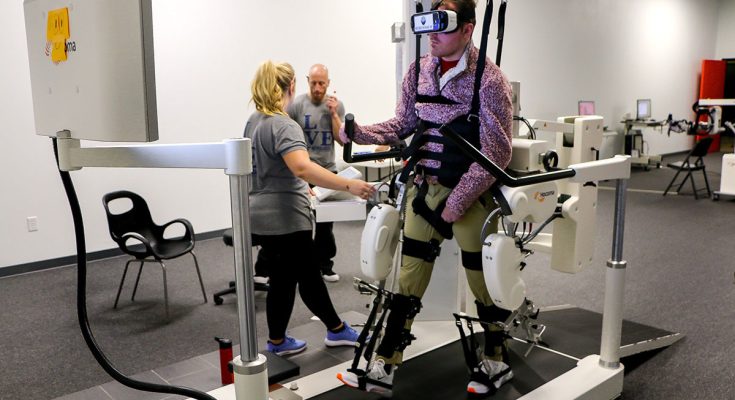
The rehabilitative Physical therapy with the use of VR is in the form of immersion and interaction while keeping the patient engaged. VR systems in the facilities are designed to stimulate similar activities as those performed by an individual in their daily routines, commonly experienced in difficulty with post-surgery or post-injury. The user partakes in physical engagement, facilitated in a computer-controlled environment. Healthcare practitioners use VR to create a world where patients can experiment with the amount of resistance to apply in their routine exercises.
Physical therapy through the VR systems usually encompasses any use of video games to achieve rehabilitation goals. Implementation of VR systems in the rehabilitation facilities involves the use of virtual reality technology coupled with motion sensors and VR headsets for total immersion of patients in an adaptable virtual world where they do physical activities. The process is gamified with some video game elements incorporated into the exercise to desist from the boring routine exercise. For instance, a client who had a stroke is exercising a skill set to his hands through exploration and his affairs with the incorporation of the system in the patient’s favorite game application.
Clinical Advantages
- Increased motivation: Video games earn millions of dollars due to their addictive gameplay. Rehab centers can use this to their advantage to ensure better rehabilitation results. Leveling and earning points help patients feel more encouraged to perform exercises.
- Immediate feedback: Virtual reality-based systems can also provide the necessary feedback to the patient. For example, a therapist can tell a patient to correct a hyper-extended knee immediately. This real-time correction function helps the patient to make the needed corrections in real-time ensuring the proper execution of exercises.
- Increased development of motor skills: By simulating specific tasks, it helps the patient develop muscle memory required to make specific movement patterns. For example, it can help Matt learn how to push off the ground with his leg and recover his walking pattern.
- Reduce pain perception: Some virtual reality-induced exercises can reduce the pain the patient feels. It is due to the phenomenon called distraction therapy. The more bearable a procedure, the longer the patient can withstand it.
Expert Insights
Interviews with physical therapists who have used the technology with patients reveal notable excitement. They affirm that the VR tools not only expand the possibilities for what can be accomplished in a session but also introduce an aspect of fun and creative novelty into treatment sessions, a gesture that seems to increase patient adherence and excitement. Statements from those who have been treated using VR echo similar sentiments. However, they indicate that some of the most challenging and boring processes have been turned into fun and engaging sessions. Nwoye and Nwoye endorse such massive psychological benefits, claiming that, “patients do not feel like they are in therapy,” and that is enough to make that specific difference in the journey towards full commitment.
On the whole, integrating VR into physical therapy or rehabilitation represents a massive leap in medical technology, allowing clinicians to better and more address cases and patient recovery. Depending on its continued advancement, we can make strides in identifying the seemingly unknown aspects of its application in healthcare. Therefore, virtually, indeed reality assurance for every patient makes it possible and affordable.